The Trust Client is the central component for communication and interaction with the TI Zero Architecture (ZTA) and must provide the following functionality:
- generation, storage and verification of a cryptographic, hardware-bound app/device identity
- generation and verification of device and app attestations using platform mechanisms and trusted third parties
- establishment of a mutually authenticated, confidential communication channel with authorized participants of the TI (over mTLS)
- management of registered apps and devices as a front-end of the GMS
With a focus on mobile devices, the Trust Client can be implemented in different ways as part of a (mobile) application:
- as part of the business logic
- encapsulated module or (native) library / SDK
- encapsulated module or (native) library / SDK from a third-party provider
Logical Components
App / Device Identity
Prior to the first use, an app accessing a service in the TI ZTA must be registered at the GMS. The app identity created during this process (cryptographic, hardware-bound key pair with associated certificate issued by GMS CA) is assigned to a user account (e.g., insured person, healthcare professional) by authenticating with the electronic health card or health ID. The app identity is used by the app via the Trust Client in the future to authenticate itself to authorized third parties in the TI (during connection establishment of the mTLS communication channel).
The Trust Client is responsible for generating, storing and verifying the cryptographic, hardware-bound app identity and uses hardware-based security mechanisms of the respective platform (Android, iOS) for implementation:
Android
- cryptographic, hardware-bound key pair (keypair_mTLS):
- ECC key pair with NIST P-256 curve
- in TEE or Strongbox KeyStore, app-bound
- proof of storage location / properties via Android Key & ID Attestation (via app-specific app attestation key material)
iOS
- cryptographic, hardware-bound key pair (keypair_mTLS):
- ECC key pair with NIST P-256 curve
- in the Secure Enclave, app-bound
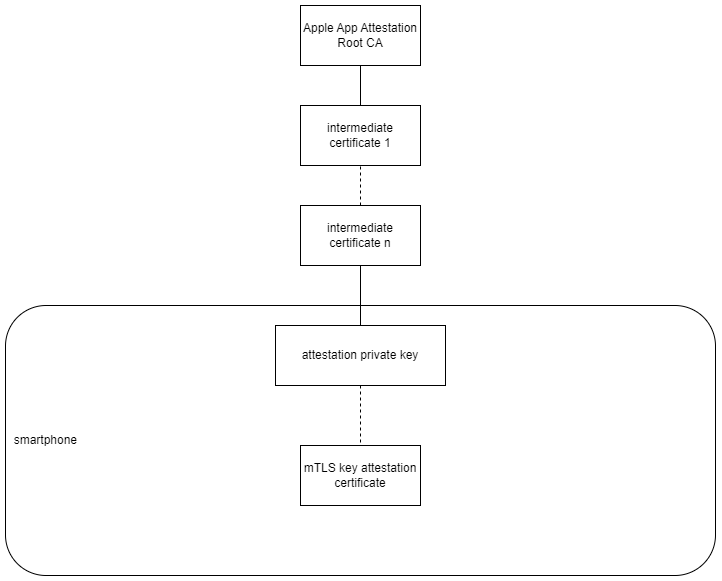
- indirect proof of storage location / properties via Apple App Attest API (pubkey_mTLS as fingerprint in the App Attest API attestation challenge)
To prove the app identity to third parties, an X.509 client certificate is generated in a further step for the key material created under Android and iOS (keypair_mTLS). This can be done in two ways:
- self-signed client certificate
- client certificate issued by a GMS CA
Device and App Attestation
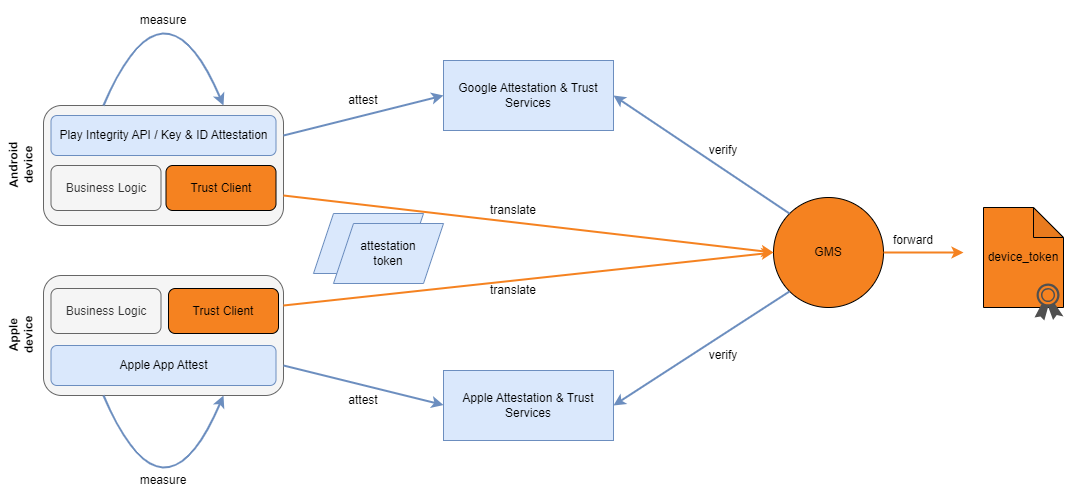
In addition to the app identity, the device’s and application’s health (Zero Trust signals) are taken into account when making an access to a resource at the PDP/PEP. The trustworthy collection of the health signals is carried out using platform-specific attestation and collection mechanisms (see Apple Platform Security Guide, Android Platform Security Model) in the TrustClient in order to guarantee the authenticity and integrity of the signals. As there is currently no standardized, cross-platform attestation format, the platform-specific attestations are converted into a consolidated device token by the GMS after checking their integrity and authenticity.
Android
Google Play Integrity API
The Play Integrity API can be used to attest the trustworthiness (integrity, authenticity) of an Android device, the Play Framework running on it and the application accessing it. The attestation is carried out after triggering an API call and made available for verification by authorized parties in form of an integrity verdict (JWT token). The verification of integrity verdicts by an authorized party (usually app developers) can be carried out remotely by sending the verdict to Google or after downloading the key material required to decrypt the verdict locally. Due to the simplicity of the attestation information provided by the Play Integrity API, it is very well suited as a low-threshold attestation. From Android 9 onwards, the actual attestation on the end device is supported by hardware security mechanisms (Android Key & ID Attestation) and is therefore of a higher assurance. Google Play Services must be installed on the Android device for the attestation process.
The Play Integrity API is used by the TrustClient to prove the general trustworthiness of the end device, the Play Services and the app to the GMS.
Android Key & ID Attestation
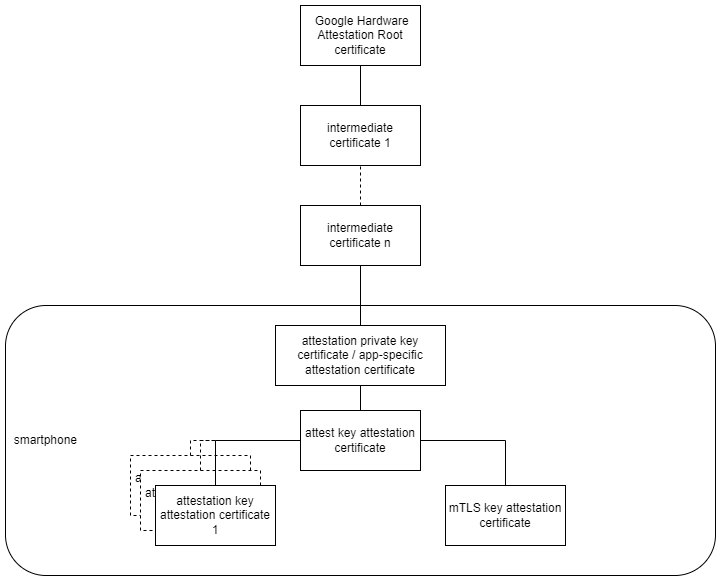
Key Attestation can be used to attest properties and the storage location (software, Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), Strongbox/TRH) of cryptographic key material generated in the Android KeyStore. Additionally, ID attestation can be used to attest the properties of a device at the time of key material generation. The actual attestation of the key material and the device properties is carried out from the TEE/TRH of a device and is signed with a platform attestation group key and certificate (Android 7 - 11) securely deployed into the device during the manufacturing. From Android 13 onwards, this group key is replaced by short-lived, app-specific attestation keys.
If an app generates cryptographic key material in the KeyStore, a X.509 attestation certificate is created and signed with the platform attestation group key. In addition, further device properties are stored in the key attestation extension data schema of the certificate before the signature is created. The X.509 certificate can now be used by third parties to check whether the key material originates from a genuine end device, in which key store it is stored and what state the end device is in.
An app-specific attestation key pair (keypair_attest) is created by the TrustClient and attested using Key & ID Attestation. Keypair_attest and the corresponding attestCert_attest now serve as the root of trust for the Trust Client, i.e. attests/signs all other cryptographic keys created in the life cycle of the Trust Client and surrounding app. This includes the app identity (keypair_mTLS, cert_mTLS), but also device and app attestations requested during resource access (keypair_attestation_n, cert_attestation_n).
Further Device Signals
In addition to the device signals from Play Integrity API and Key & ID Attestation, Android System API calls can be used to collect further valuable properties of a device. This information is is collected in the application during runtime. For more information see DSR-RFC-06 or Android Zero Trust Signals.
iOS
With App Attest, part of the DeviceCheck framework, Apple provides a native API that makes it possible to verify the authenticity and integrity of Apple devices and apps via a hardware-bound key pair and an associated attestation or assertion in accordance with the W3C WebAuthn specification. In contrast to Android Key & ID Attestation, this key pair can only be used to sign challenges.
Further Device Signals
Similar to Android , there are further valuable device and app properties that can be collected by using additional system APIs. For more information see DSR-RFC-06.
Communication Channels
Trust Client to GMS
The Trust Client communicates directly or via the surrounding app with the GMS. In either case, the Trust Client provides the cryptographic key material required for secure communication (TLS, mTLS), including the attestation and session tokens:
- App registration: When initial contact is made with the GMS, no app identity or key material for mTLS client authentication yet exists in the Trust Client. The GMS therefore offers a standard TLS endpoint for registration.
- App attestation & device management: After successful registration with the GMS, the Trust Client holds key material for mTLS client authentication (keypair_mTLS). All GMS endpoints outside the registration are therefore only available via mTLS.
Trust Client to Health Service
The Trust Client communicates directly or via thesurrounding app with the health service. In either case, the Trust Client provides the cryptographic key material required for secure communication (mTLS).